- Category: Articles
Integration of Data Analytics to Enhance Turbine Reliability
 In the ever-evolving landscape of renewable energy, offshore wind farms are pivotal for achieving sustainability goals. However, the economic feasibility of these farms is often hampered by higher operational costs and the cost of energy compared with onshore wind energy and conventional power sources. This article sheds light on how advancements in condition monitoring and wake optimisation are set to improve the industry. It discusses the integration of data analytics to enhance turbine reliability, alongside approaches to improve turbine efficiency through advanced control techniques. This discussion not only underscores the importance of continuous innovation in the renewable energy sector but also highlights the potential for significant cost reductions and efficiency improvements in wind energy projects.
In the ever-evolving landscape of renewable energy, offshore wind farms are pivotal for achieving sustainability goals. However, the economic feasibility of these farms is often hampered by higher operational costs and the cost of energy compared with onshore wind energy and conventional power sources. This article sheds light on how advancements in condition monitoring and wake optimisation are set to improve the industry. It discusses the integration of data analytics to enhance turbine reliability, alongside approaches to improve turbine efficiency through advanced control techniques. This discussion not only underscores the importance of continuous innovation in the renewable energy sector but also highlights the potential for significant cost reductions and efficiency improvements in wind energy projects.By Pieter-Jan Daems, Cédric Peeters and Jan Helsen, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Belgium
- Category: Articles
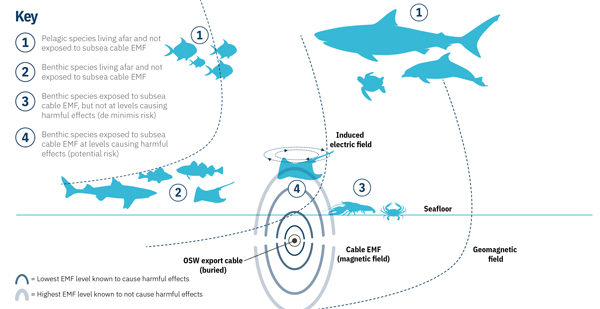 Harnessing an Agent-Based Model to Support Impact Assessments
Harnessing an Agent-Based Model to Support Impact AssessmentsOffshore wind (OSW) is an important component of the transition to renewable energy in the USA. OSW projects generate electromagnetic fields (EMFs), which may impact marine organisms. In pre-construction assessments of these impacts, modelled EMFs are compared with literature-derived effect thresholds for sensitive marine organisms. However, it is frequently unclear whether some literature-derived effects are meaningful at a population level. In the absence of data, biologically detailed models, such as agent-based models (ABMs), can tie exposure and effects together. Here, we describe an ABM that simulates an electrosensitive organism, little skate, swimming in the presence of a direct-current magnetic field generated by undersea OSW cables. The model simulates behavioural effects from EMF exposure on individuals in a modelled population and translates the effects into an energetics basis, providing a quantifiable metric of the effect of exposure on population viability. Through a proof-of-concept application, we show that ABMs can help support EMF impact assessments by helping to evaluate potential exposure effects in a context relevant to fisheries management.
By Daniel Dawson and Damian Preziosi, Integral Consulting, USA
- Category: Articles
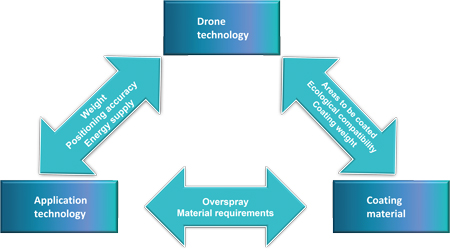 Temporary and Environmentally Friendly Coating with Drones
Temporary and Environmentally Friendly Coating with DronesIcing of wind turbines is a major problem in their operation, as it leads to massive yield losses and wear and tear and endangers people in the vicinity. De-icing using helicopters or industrial climbers is extremely time-consuming. Turbine operators who want to protect their wind turbines from icing have had to dig deep into their pockets – heating mats or systems that can be integrated into the blades, systems that pump warm air into the rotors, or the use of lifting helicopters that spray de-icing agents are all associated with high costs. Drones, only used when necessary, offer an inexpensive alternative.
By Andreas Stake and Oliver Tiedje, Fraunhofer, Germany
- Category: Articles
How Can Ecological Modelling Support the Sustainable Development of Offshore Wind?
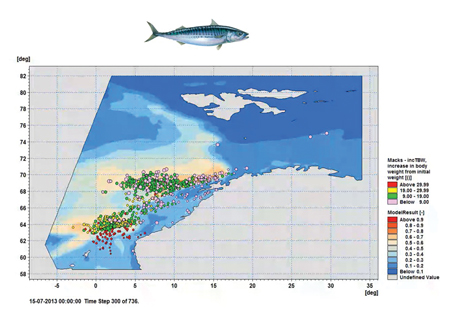 The plans to establish offshore wind farms globally have become increasingly ambitious and will lead to impacts on marine life, such as fish and marine mammals. Such impacts must be predicted and managed so that planned projects can go ahead while simultaneously minimising environmental footprints. Dynamic ecological modelling can simulate baseline conditions and impacts from various stressors, for example underwater noise, using the most accurate representation of animals, including their movements and reaction to said stressor. With such models, environmental issues can be identified early and throughout the project cycle to allow integrated mitigation solutions, easing the environmental approval processes and reducing related scheduling and investment risks.
The plans to establish offshore wind farms globally have become increasingly ambitious and will lead to impacts on marine life, such as fish and marine mammals. Such impacts must be predicted and managed so that planned projects can go ahead while simultaneously minimising environmental footprints. Dynamic ecological modelling can simulate baseline conditions and impacts from various stressors, for example underwater noise, using the most accurate representation of animals, including their movements and reaction to said stressor. With such models, environmental issues can be identified early and throughout the project cycle to allow integrated mitigation solutions, easing the environmental approval processes and reducing related scheduling and investment risks.By Frank Thomsen, Lars O. Mortensen, Naomi A.M. Tuhuteru, Jonas B. Mortensen, DHI, Denmark
- Category: Articles
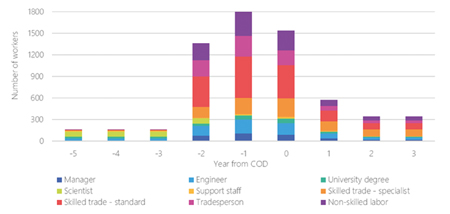 Early Strategic Planning for a Diverse and Local Offshore Wind Workforce
Early Strategic Planning for a Diverse and Local Offshore Wind WorkforceState and federal policies have incentivised offshore wind developers to think locally for their workforce and supply chain. New manufacturing facilities, installation ports, and projects will create a demand for local workforces, both in the general trades, the unions, and specialised job roles specific to offshore wind. This article discusses why early strategic planning is critical for training a new industrial workforce in alignment with the pace of market demand.
By Nick Zenkin, Lead Offshore Wind Consultant, Xodus Group, USA
- Category: Articles
 MX-System
MX-SystemThe MX-System from Beckhoff is a flexible, space-optimised system solution that can replace conventional control cabinets, thereby opening up new possibilities in wind turbine automation. As a modular control cabinet replacement that can also be decentralised inside the wind turbine if required, the MX-System saves engineering, assembly, installation, and maintenance effort. This enables highly efficient processes for the manufacturers and operators of wind turbines – from the planning, set-up and installation of the MX-System through to the maintenance of MX-System-equipped turbines.
By Andreas Franke, Business Manager Wind Energy, Beckhoff Automation, Germany
- Category: Articles
 A Step Towards Mitigating Wind Turbine Annoyance
A Step Towards Mitigating Wind Turbine Annoyance‘What is their problem, really?’ This question has been voiced by developers and operators of wind power, as it relates to citizens who complain of annoyance from wind turbines. ‘After all, most people are not annoyed, and they recognise how important development of wind resources is to combat climate change,’ we hear. Sometimes, the statement is more forceful: ‘most normal people are not annoyed,’ implying somewhat harshly that there may be something abnormal with those annoyed. When one makes a conscientious effort to communicate with people expressing annoyance, one finds they are neither malcontents nor oblivious to climate change concerns. Yet, one hears them express words such as, ‘I just haven’t been able to stand it in my home since the wind turbines were installed.’ For those impacted, annoyance is not merely a temporary unpleasant phenomenon but a condition that adversely impacts their life and health.
By William K.G. Palmer, Independent Researcher, Canada
Use of cookies
Windtech International wants to make your visit to our website as pleasant as possible. That is why we place cookies on your computer that remember your preferences. With anonymous information about your site use you also help us to improve the website. Of course we will ask for your permission first. Click Accept to use all functions of the Windtech International website.










