- Details
- Category: Articles
 Where There’s Wind, There’s Often a Surplus of Transmission Capacity
Where There’s Wind, There’s Often a Surplus of Transmission Capacity
In 2023, Minnesota-based power collective Great River Energy completed a two-year study designed to identify the sources of congestion with the highest financial impact on its operations. It not only wanted to decrease costs, it wanted to figure out how to unlock untapped capacity on the congested lines.
By Jørgen Festervoll, CEO, Heimdall Power, Norway
- Details
- Category: Articles
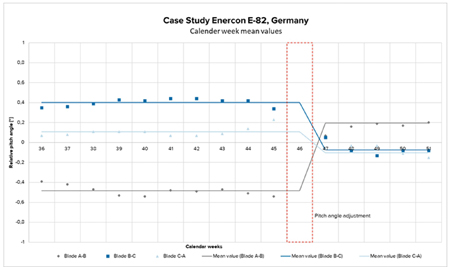 Maximising Energy Production and Reducing Fatigue
Maximising Energy Production and Reducing Fatigue
Proper blade alignment in wind turbines is crucial for maximising energy production and reducing fatigue. This article explores a system that addresses pitch misalignment, enhancing turbine efficiency and longevity by ensuring each blade is pitched at the same angle. Pitch misalignment in wind turbines can significantly impact performance. When the blades are not uniformly pitched, it results in decreased aerodynamic efficiency and increased mechanical stress. Various factors can cause blade pitch to become misaligned, such as wear and tear on mechanical components, temperature variations, and human error during maintenance.
By Matthew Stead, Chief Product Officer and Co-Founder, eologix-ping, Australia
- Details
- Category: Articles
Climate Change Impact on Yield-Relevant Parameters and Annual Energy Production
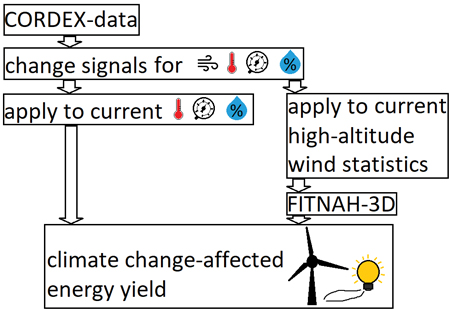 The question of how climate change will affect the energy yield of wind farms during their operating period has been increasingly raised at conferences and industry meetings. However, when determining wind potential, wind data from the past is generally used to determine the average wind and energy yield conditions to be expected during the future operating period of the planned wind farm. This is done under the assumption that the wind conditions of the past will also exist in the future. To consider climate change, GEO-NET studies its impact on the yield-relevant quantities and thus estimates the future yield of wind farms using various climate scenarios. The estimation is based on the coupling of an ensemble of regional climate projections from the CORDEX initiative for various representative concentration pathway scenarios with the computational fluid dynamics model FITNAH-3D. Exemplary results of the applied method are given, and their significance is discussed.
The question of how climate change will affect the energy yield of wind farms during their operating period has been increasingly raised at conferences and industry meetings. However, when determining wind potential, wind data from the past is generally used to determine the average wind and energy yield conditions to be expected during the future operating period of the planned wind farm. This is done under the assumption that the wind conditions of the past will also exist in the future. To consider climate change, GEO-NET studies its impact on the yield-relevant quantities and thus estimates the future yield of wind farms using various climate scenarios. The estimation is based on the coupling of an ensemble of regional climate projections from the CORDEX initiative for various representative concentration pathway scenarios with the computational fluid dynamics model FITNAH-3D. Exemplary results of the applied method are given, and their significance is discussed.
By Simone Pfau, GEO-NET Umweltconsulting, Germany
- Details
- Category: Articles
 High-Altitude Modular Post-Tensioned Concrete Wind Towers
High-Altitude Modular Post-Tensioned Concrete Wind Towers
In the race for efficiency and innovation, the wind energy sector is rethinking the very shape and logistics that define its towering giants. The industry has focused on the circular shape for towers because of its low aerodynamic drag coefficient. What if, thinking outside the box, this shape were dropped from the overall design and a new approach similar to buildings was accessed? Imagine wind towers that rival the height of city landmarks, harnessing greater wind capacities while revolutionising transportation logistics. Could these giants be modular, swiftly transported like ubiquitous shipping containers, seamlessly moving across road, rail, oceans and even the skies? The challenge extends beyond mere height – it is about speed and scalability. Can wind towers be prefabricated in factories and assembled with automotive efficiency? These questions push boundaries, urging us to shatter conventional paradigms while leveraging the very strengths of standardised container logistics.
By Andrés de Antonio, Aeventor, USA
- Details
- Category: Articles
What Is the Industry Willing to Accept to Confront It?
 Floating lidar systems have revolutionised the offshore wind industry by enabling the bankability of projects at a fraction of the original cost – successful wind resource assessment campaigns are essential for the economic viability of the wind farm development process. However, one parameter measured in such campaigns – turbulence intensity – is at the centre of debate. Its accuracy, with respect to the traditional definition, is known for not reaching industry standard levels, representing a serious problem because of the lack of consensus within the industry on how to address and solve this matter. The complexity of this phenomenon means that there is no optimal solution. Several suboptimal alternatives are currently under development, but there is not yet a clear picture of which is the right option. However, this might be about to change.
Floating lidar systems have revolutionised the offshore wind industry by enabling the bankability of projects at a fraction of the original cost – successful wind resource assessment campaigns are essential for the economic viability of the wind farm development process. However, one parameter measured in such campaigns – turbulence intensity – is at the centre of debate. Its accuracy, with respect to the traditional definition, is known for not reaching industry standard levels, representing a serious problem because of the lack of consensus within the industry on how to address and solve this matter. The complexity of this phenomenon means that there is no optimal solution. Several suboptimal alternatives are currently under development, but there is not yet a clear picture of which is the right option. However, this might be about to change.
By Adrià Miquel and Giacomo Rapisardi, Eolos Floating Lidar Solutions, Spain
- Details
- Category: Articles
Data Availability Impacts Uncertainty of Long-Term Corrected Wind Surprisingly Little
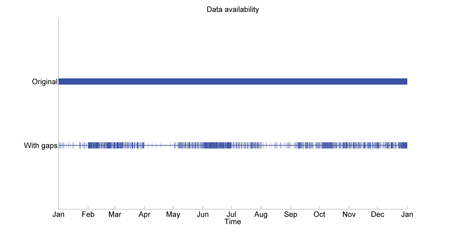
According to common guidelines for the evaluation of site-specific wind conditions, a measurement campaign should have at least 90% data availability during a consecutive 12-month period in order to be complete. However, obtaining this high data availability with a Doppler lidar can be a challenge in locations with small amounts of atmospheric aerosols, for example in the Nordic countries or mountainous regions. Regardless of the lower data availability, the data measured in these locations can still hold valuable information that can be used to reduce uncertainties in a wind resource assessment. Therefore, we suggest that instead of discarding data with less than 90% data availability, the uncertainties due to the lower lidar data availability should be quantified and considered in the wind resource assessment. This is in line with the upcoming IEC framework for the assessment and reporting of the wind resource and energy yield.
By Pyry Pentikäinen, Adviser, Kjeller Vindteknikk, Finland
- Details
- Category: Articles
Windborne to Identify Yaw Misalignments Across a Large Fleet of Wind Turbines
 According to a technical report by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (referring to the multi-year Wind Plant Performance Prediction project), modern wind power plants in the United States were underperforming in their expected annual energy output by 3.5%–4.5%.’ [1] There are many potential causes of wind turbine underperformance. Among these are forms of underperformance caused by rotor-disrupted and/or poorly calibrated nacelle-based wind sensors that in turn feed inaccurate wind data to core wind turbine systems.
According to a technical report by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (referring to the multi-year Wind Plant Performance Prediction project), modern wind power plants in the United States were underperforming in their expected annual energy output by 3.5%–4.5%.’ [1] There are many potential causes of wind turbine underperformance. Among these are forms of underperformance caused by rotor-disrupted and/or poorly calibrated nacelle-based wind sensors that in turn feed inaccurate wind data to core wind turbine systems.
By Itay Mor, Boaz Peled, Alex Alpert, and Guy Yakir at First Airborne, Israel
Windtech International wants to make your visit to our website as pleasant as possible. That is why we place cookies on your computer that remember your preferences. With anonymous information about your site use you also help us to improve the website. Of course we will ask for your permission first. Click Accept to use all functions of the Windtech International website.









